A Step By Step Guide to Pre-translation
You know that saying “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure”?
Well, it would seem that statement rings true even when it comes to the process of translation.
According to Daniel Gouadec, author of Translation as a Profession, most translation problems can be prevented by getting as much information as possible prior to a translation project.
Therefore, it only makes sense for businesses to invest more resources in the very first translation process step: Pre-translation.
So, let’s take a look at what pre-translation entails and how you can better tackle this step in the translation process to save your team time and effort, prepare your systems for modern automation opportunities, and beyond.
Where Does Pre-Translation Fit Into the Translation Process Steps?
Translation is essentially the process of converting a chunk of content from one language (the source language or “SL”) to another language (the target language or “TL”).
And this translation process involves a series of activities that fall into three phases: Pre-translation, translation, and post-translation.
While each of the translation process steps is of course important, today we’re going to focus on that first one, as it lays the foundation for all further translation efforts.
Pre-translation is all the preparation that takes place up to the moment the translator receives all the materials and resources for translation.
What does that look like?
In the pre-translation phase, businesses should be thinking about things like how the technical architecture of their website or app will impact translation, how translation will influence the specific project at hand, what they can include in their glossary and translation memory to help translators save time and avoid mistakes, and plenty more.
We’re going to show you exactly how to step through the above considerations and more to create an effective pre-translation process — right after we get done telling you why it’s so important for you to care.
Why Is Pre-Translation One of the Most Vital Translation Process Steps
An investment in pre-translation is an investment in the success of not just your content but your entire business.
Here’s why.
Minimize Mistakes That Could Negative Impact Your Brand
When you’re competing on a global stage, your ability to deliver on consumer expectations is key.
And what is it that consumers expect?
Well, for starters, they expect content to be in their native tongue!
With a well-executed pre-translation process that takes localization (which is the process of adapting your content for a specific locale) into account from the very beginning, you’ll be prepared to create translations that speak to consumers on a personal level and put your brand well ahead of the competition.
Make the Translation Process Faster — And Therefore More Affordable
In the translation field, many professionals charge by the word. If you want to make their workflow faster — which in turn makes it more affordable for you — you must conduct a thorough pre-translation process that works out the kinks in both your linguistics and your technology so their job simply flies by.
Increase Automation Across the Translation Process
As we’ll discuss more later, there are plenty of pre-translation process steps that can be aided by modern automation. However, since automation depends on smart machines that rely on patterns and rules, it only works in well-organized systems where assets are labeled and searchable.
This means a pre-translation process that focuses on developing a clear and straightforward path to translation is the only thing that makes it possible to take advantage of automation throughout the translation process.
Pre-Translation Process Steps: Your Complete Guide
If you’re a translation project owner and your head is spinning as you wonder how to even get started with pre-translation — take a breather.
Allow us to guide you through all the major steps you should take to prepare your next translation project for success.
Step 1: Separate Text (Strings) from Code
Oftentimes, the localization and translation process steps are complicated because your app’s UI strings aren’t optimally organized.
If that’s the case for you, here’s what your development team needs to do.
Move All Text Into a String File
To make translation and localization straightforward, first separate string resources from your code and markup to create a single language-independent codebase.
Hard coding any strings will make it difficult to translate and localize. Instead place all the strings into a resource file, like a .strings or .xml file, so your strings can be extracted, translated, and integrated back into your app without any changes to compiled code.
Provide Sufficient Context for Declared Strings
When declaring strings in your resource file, make sure to describe the context clearly in which the string is used. For example: What is this string for? When and where is it showed to the user? Is it a button or a text box?
This kind of contextual information is critical to translators to produce better quality translations.
Mark Anything That Should Not Be Translated
Over-translation and -localization is a common source of problems. To avoid this, ensure that only strings that need to be translated are provided to translators. And if certain parts of a string shouldn’t be translated to other languages (e.g. a piece of code, a placeholder for a value, a special symbol, etc.), mark it to remain “as-is” so that translators don’t touch it.
Find out more about strings, translation, and localization in this blog.
Step 2: Make Sure You’re Prepared to Support Plural Forms
The next important, but often overlooked, pre-translation process step is making sure to support plural forms.
Different languages have different rules for the formation of plurals. For example, English has two forms: A singular form for “one” (e.g. 1 book) and a plural form for “everything else, including zero” (e.g. n books).
While this is fairly simple in English, other languages make finer distinctions. For instance, Russian has different plural forms for numbers ending in 1 (except 11), numbers ending in 2 to 4 (except 12 through 14), and other numbers. When it comes to pre-translation, project owners and developers need to be aware of these very important linguistic nuances.
While deciding which case to follow for a given language and quantity can be complex, linguistic plurals are a key part of creating high-quality multilingual products that are relevant to local cultures.
Step 3: Conduct Pseudo-Localization
Pseudo-localization, which is performed during the product development phase, is the process of replacing the text of a product with a dummy translation instead of a professional translation. What this does is give a “feel” for what a translated and localized product will look like before it’s totally finished.
Pseudo-localization is a cost effective way of identifying usability and functionality bugs that will hinder translation and finding out how prepared your product is for localization. This testing method can reveal hard-coded strings that should be translatable, find strings that shouldn’t be translated, and identify design/layout issues that will affect the translated product in the future.
Generally speaking, the earlier you can identify translation problems by using a process like pseudo-localization, the faster and less costly it will be to address and reverse them.
Step 4: Build Your Translation Glossary
In every project, there are usually a few key terms that define the product. You need to make sure these terms are translated accurately and consistently in every use case. This is where a glossary — sometimes called a terminology database or termbase — comes into play.
A good translation glossary eliminates ambiguity and serves as a guide for translators on how to manage key terminology. After generating a list of key terms (e.g. acronyms, names, titles, subject-specific terminology, and more) and providing clear definitions and proper context, project owners should also work closely with translators to review and approve the final translations.
When translators are working in a CAT tool, these key terms will be highlighted together with the pre-approved translations to enhance consistency and accuracy. In cases where there is a high volume of repetition, it can save both time and money as well.
Keep reading about the ins and outs of translation glossaries here.
Step 5: Use Translation Memory
Translation memory (TM) software acts like a database that stores and draws information from previously translated content.
Similar to a glossary, TM software maintains consistent translation throughout the project.
So what’s the difference between translation memory software and a glossary? A glossary is a guide for translators on how to translate specific key terms whereas translation memory software automatically translates repetitive content, eliminating the need to re-translate the same text in current or previous projects. Up-to-date translation memory software is key to reducing the time it takes to complete translation projects and can also help make sure translations are consistent and accurate.
In fact, translation memory software has been shown to reduce translation costs by as much as 30% and grow translation productivity by much more!
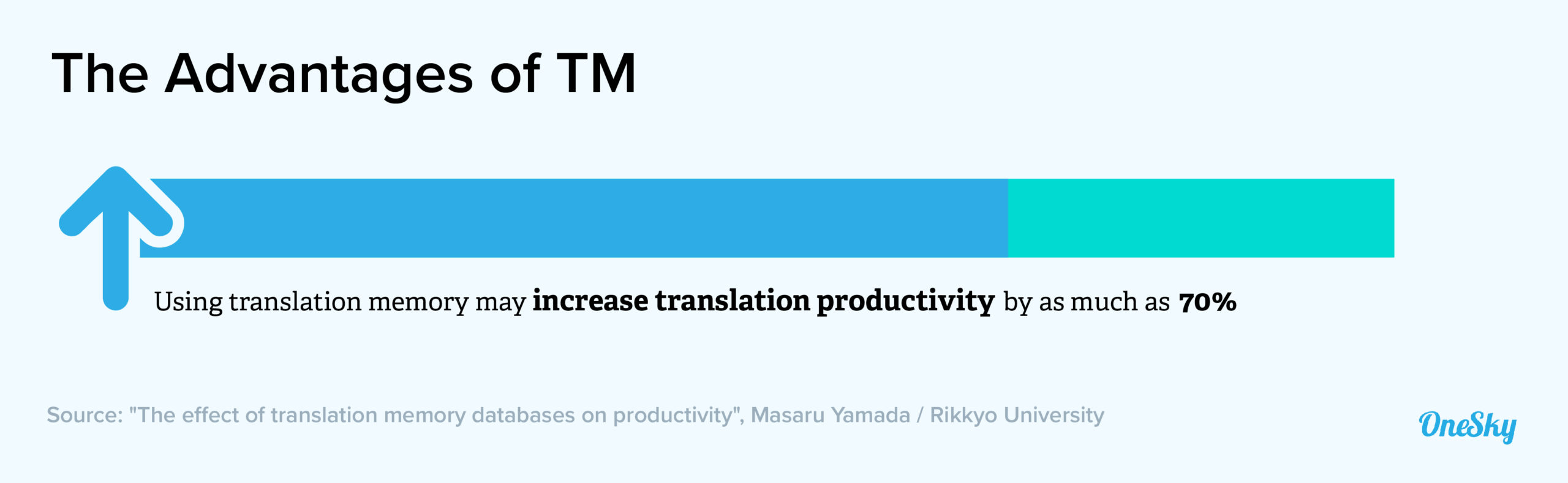
Learn the key benefits of translation memory software from this guide.
Step 6: Create a Style Guide
Impactful translation isn’t just about taking your content from one language to another, word-for-word. It also includes localization, which means updating your content to align with a location’s unique culture, preferences, laws, syntax, pop culture references, and more.
Therefore, project owners are recommended to prepare a style guide that takes both translation and localization into consideration before starting a translation project. This guide will serve as a framework for translators to understand the company’s voice, personality, and brand goals — no matter to which culture group they’re speaking. A consistent translation voice can be achieved if all the translators involved in the project follow these guidelines as closely as possible.
Typical elements in the style guide include:
- Punctuation and grammar rules (spacing, quotation marks, etc.)
- Branding elements (names, unique terms, etc.)
- Formatting (bolding, fonts, trademarks, etc.)
- Localization adaptations (how to address currencies, addresses, phone numbers, etc.)
To see how localization and translation play together, check out this helpful article.
Step 7: Provide Contextual Information
We’ve finally made it to the last of our pre-translation process steps.
In a poorly-organized translation project, translators have to work with anonymous strings in a translation tool without looking at the actual product, which increases the chance of contextual errors and excessive project management time.
As the project owner, if you don’t want your translators to do guesswork, you need to provide them with a sufficient amount of reference materials. While things like screenshots and examples are nice, it’s highly recommended to let translators use the actual product during the project, if possible.
These kinds of resources allow translators to see their work in context, so they can adjust the text length or translation meaning in the best possible way. The most helpful resources should even indicate where the associated strings are located on the screen and all necessary elements that may influence the translation process.
For more tips on making translation faster, better, and more affordable — click here.
How Will You Tackle the Most Important Translation Process Steps: Pre-Translation?
It’s true that setting up your pre-translation process the right way will take a little bit of time, but in the end we swear it’ll be worth it.
Pre-translation is perhaps the most important of all the translation process steps. This is because it prepares your content and therefore your business for success by laying a foundation for helpful automations, fast yet accurate and affordable translation, a great brand reputation across countries, and more.
If you’re ready to tackle translation and localization on your own, download our free, 53-page ebook “The Essential Guide to App Localization” and learn how to build tech that’s translation-ready from the ground up, how to pick the best new markets to move into, and more.
Or, if you’re looking for support from the most complete localization and translation solution in existence today, check out how OneSky’s management platform works and then sign up to begin using OneSky — it’s free to start.




 Written by -
Written by - 




 Written by
Written by 


